-

Company
Product
ALUMINIUM MACHINES
PORTABLE MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINUM
PORTABLE COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
PORTABLE END MILLING MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
AUTOMATIC MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
END MILLING MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
ALUMINUM CORNER CRIMPING MACHINE
DOUBLE MITRE SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
AUTOMATIC SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
BAR PROCESSING CENTERS
MACHINING CENTERS FOR ALUMINIUM COMPOSITE PANELS
NOTCHING SAWS
WEDGE CUTTING SAWS AND NOTCH CUTTING SAWS
MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
PVC PLASTIC MACHINES
PORTABLE MITER SAWS FOR PLASTIC
PORTABLE COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
PORTABLE END MILLING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
MITER SAWS FOR PLASTIC
COPY ROUTERS FOR PLASTIC
END MILLING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
WELDING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
CORNER CLEANING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC PROFILES
DOUBLE MITRE SAWS FOR PLASTIC
BAR PROCESSING CENTERS
GLAZING BEAD SAWS
AUTOMATIC MITRE SAWS FOR PLASTIC
METAL MACHINES
MANUAL METAL SHEET BENDING MACHINE
MANUAL BENDING MACHINES
HYDRAULIC BENDING MACHINES
NON MANDREL BENDERS
PLATE BENDING MACHINES
BORDERING AND TRIMMING MACHINES
HORIZONTAL PRESSES
BELT GRINDING MACHINES
PIPE NOTCHING MACHINES
PIPE POLISHING MACHINES
LASER CUTTING MACHINES
PRESS BRAKES
VERTICAL TURNING CENTERS
MACHINING CENTERS
WOOD MACHINES
GLASS MACHINES
ROBOTICS SPECIAL MACHINERY
Service
Blog
Contact
Blog
- Home
- Blog
- ALUMINIUM PROFILE SAW MACHINE
- DOUBLE-HEAD MITRE SAW
DOUBLE-HEAD MITRE SAW

Double-Head Mitre Saw – Scientific Consideration of a Key Technology for Profile Cutting
1. Introduction
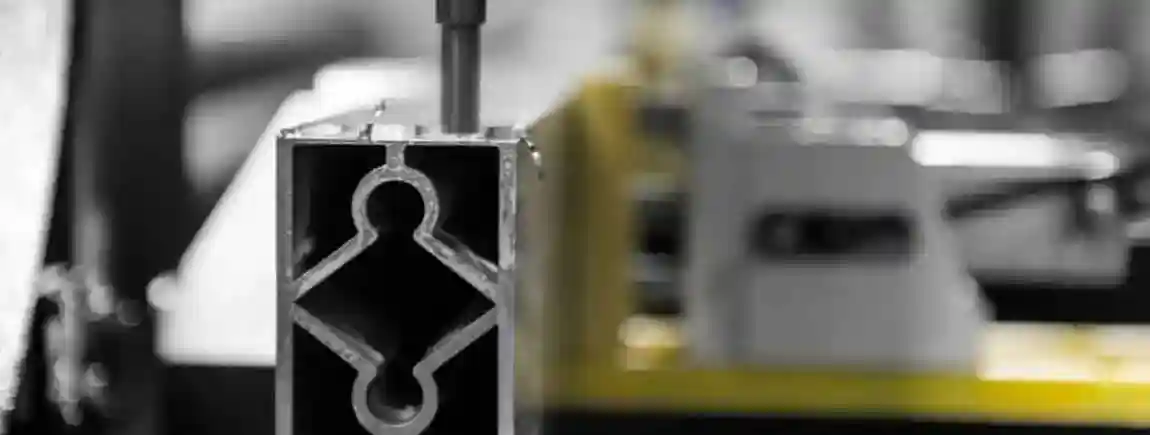
The double-head mitre saw is a highly specialised machine tool primarily used in the processing of aluminium, plastic, and wood profiles. Its development is closely linked to the industrialisation of window, door, and façade production. By enabling simultaneous machining of workpieces from both ends, it achieves maximum precision, efficiency, and repeatability.
2. Historical Development
The origins of the mitre saw lie in traditional craftsmanship, where simple hand saws were used for wood joints at 45° or 90°. With the industrial demand for precise profile connections in construction, the first generation of double-head mitre saws was developed in the 1960s. The introduction of CNC technology in the 1980s marked the decisive step towards automation and integration into digital manufacturing processes.
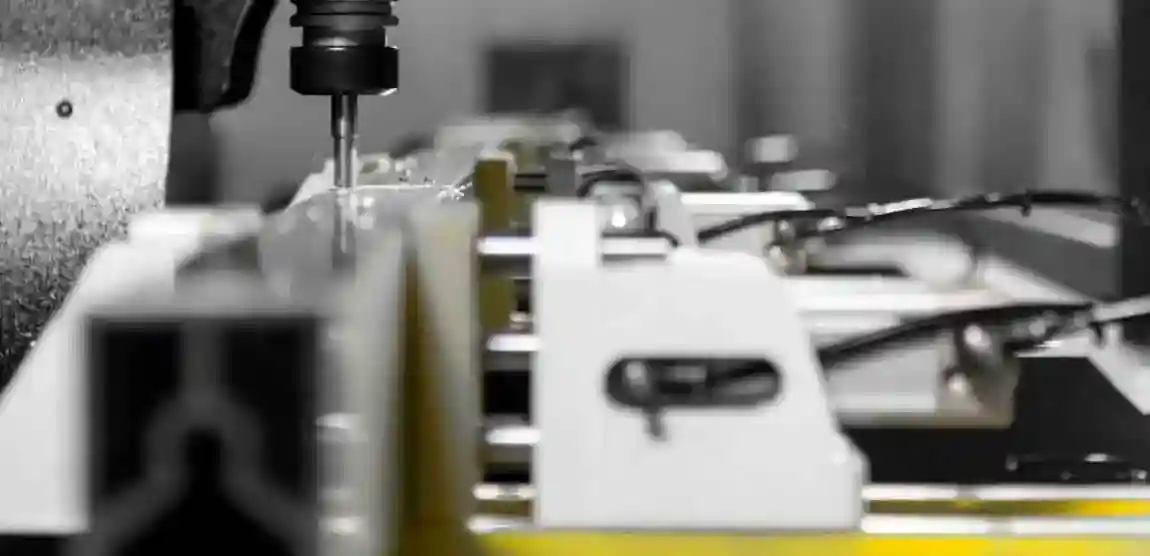
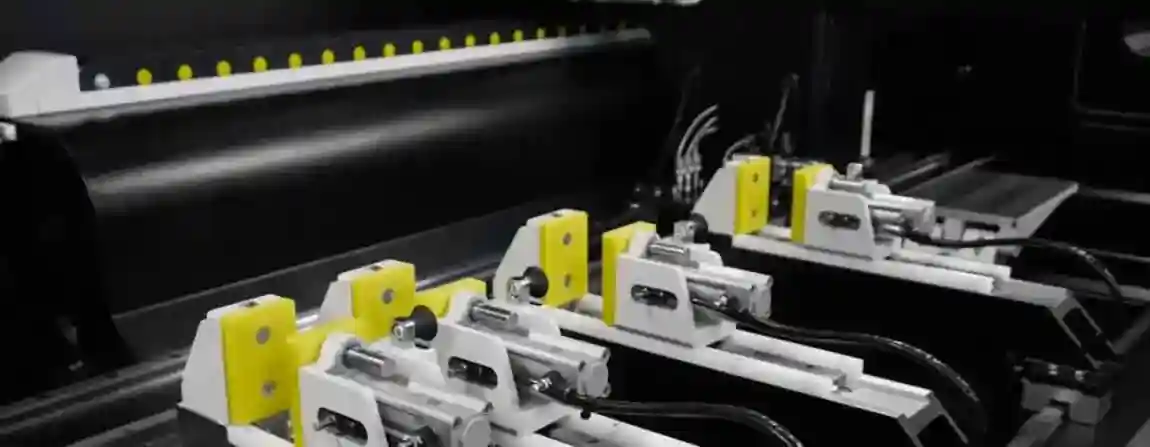
3. Constructional Features
A double-head mitre saw typically consists of:
-
A machine bed with a high-stiffness design to minimise vibrations.
-
Two saw heads that can operate synchronously or separately.
-
Swivel mechanisms enabling mitre cuts between 45° and 135°.
-
A CNC control unit allowing input of cutting parameters and import of CAD/CAM data.
-
Clamping systems, usually pneumatic, for secure workpiece fixation.
4. Functionality
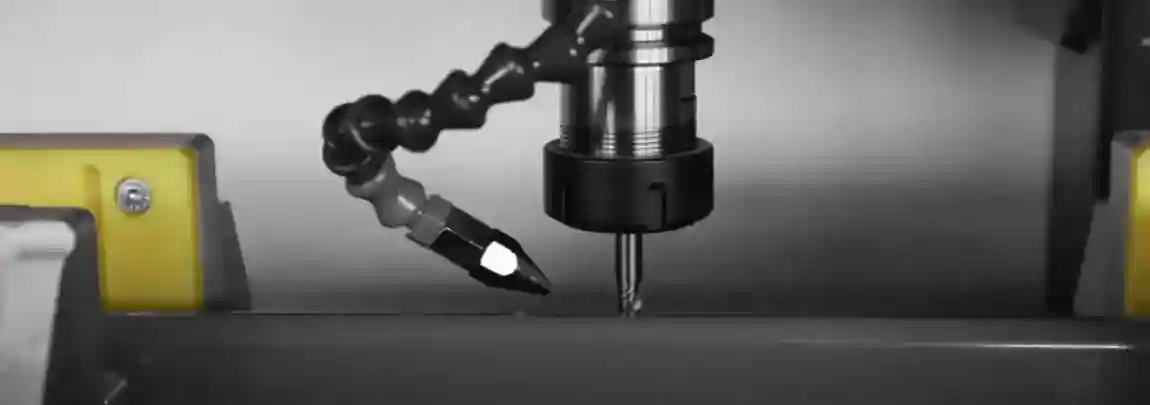
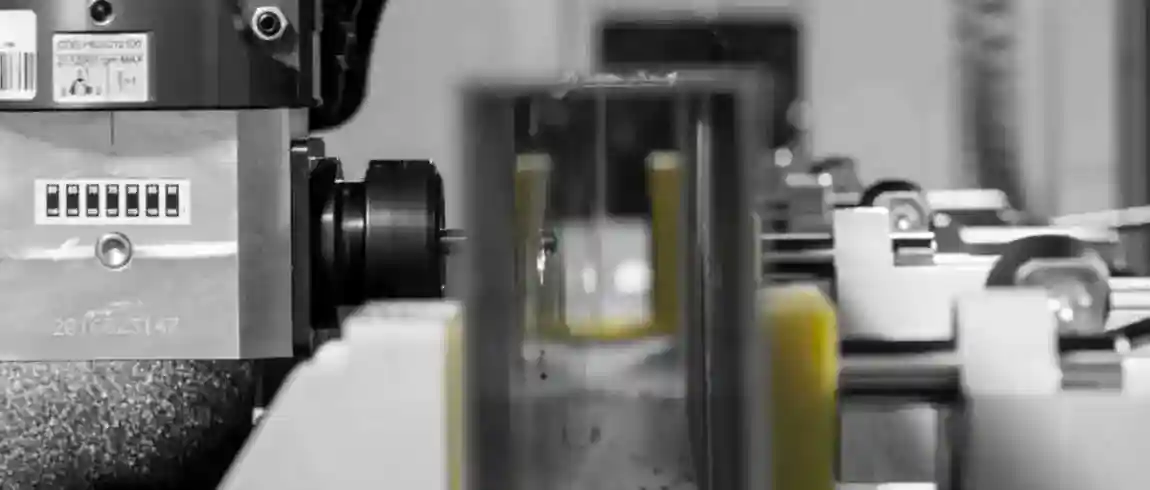
The workpiece is clamped between the two saw heads. After inputting the cutting data, the heads automatically move into position. Cutting takes place simultaneously or sequentially, ensuring dimensional accuracy within hundredths of a millimetre. Cooling systems or minimum quantity lubrication reduce friction and increase tool life.
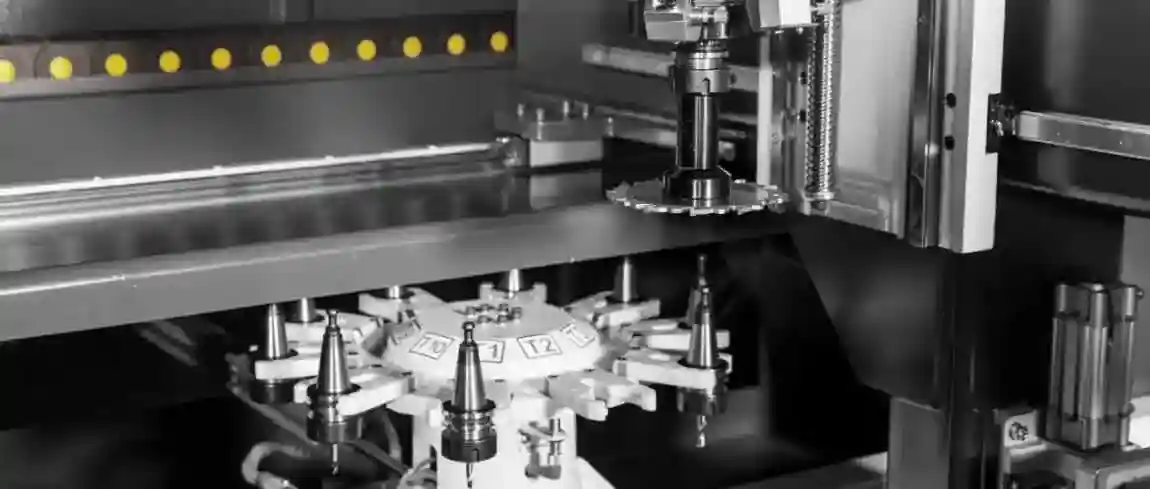
5. Tools and Cutting Technology
The carbide saw blades used have diameters of 400–600 mm and are specifically designed for aluminium and plastic. Their tooth geometry is optimised depending on the material. Modern systems feature sensor-based monitoring to detect tool wear and automatically make adjustments.
6. Fields of Application
The double-head mitre saw is used in various industries:
-
Window and door construction: cutting frame and sash profiles.
-
Façade construction: production of precise connecting profiles for glass and metal façades.
-
Furniture and lightweight construction: processing of aluminium and wooden frames.
-
Mechanical engineering: cutting special profiles for plant construction.
7. Advantages and Scientific Evaluation
Compared to single-head mitre saws, the double-head mitre saw offers clear advantages:
-
Precision: CNC-controlled positioning significantly reduces tolerances.
-
Efficiency: simultaneous cuts reduce cycle times by up to 50%.
-
Flexibility: adaptable to different materials and profile cross-sections.
-
Sustainability: optimised cutting plans minimise waste and energy consumption.
From a scientific perspective, the machine exemplifies the synergy of mechanics, electronics, and computer science.
8. Integration into Industry 4.0
The future of the double-head mitre saw lies in networking:
-
IoT interfaces enable real-time monitoring of production data.
-
AI algorithms optimise cutting sequences and tool changes.
-
Predictive maintenance reduces downtime through proactive servicing.
-
Digital twins allow full process simulations.
9. Economic Significance
Investment in a double-head mitre saw pays off quickly due to efficiency gains. Studies show production capacities can increase by up to 60% while scrap rates decline. This makes the machine an indispensable component of modern manufacturing.
10. Conclusion
The double-head mitre saw is not just a tool but a key technology in profile processing. It combines precision, efficiency, and future viability. From a scientific viewpoint, it exemplifies the shift from traditional manufacturing methods to highly automated and digitally networked production systems.
- double head mitre saw
- double head mitre saw aluminium
- double head mitre saw plastic
- double head mitre saw wood
- cnc double head mitre saw
- automatic double head mitre saw
- industrial double head mitre saw
- precision double head mitre saw
- double head mitre saw for profile processing
- double head mitre saw for windows
- double head mitre saw for doors
- double head mitre saw for façades
- double head mitre saw for mechanical engineering
- double head mitre saw for furniture
- double head mitre saw for lightweight structures
- double head mitre saw new
- double head mitre saw used
- double head mitre saw evomatec
- double head mitre saw industry 4.0
- double head mitre saw cnc technology
 GERMANY
GERMANY ENGLISH
ENGLISH FRANCE
FRANCE SPAIN
SPAIN PORTUGAL
PORTUGAL