-

Company
Product
ALUMINIUM MACHINES
PORTABLE MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINUM
PORTABLE COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
PORTABLE END MILLING MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
AUTOMATIC MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
END MILLING MACHINES FOR ALUMINIUM
ALUMINUM CORNER CRIMPING MACHINE
DOUBLE MITRE SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
AUTOMATIC SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
BAR PROCESSING CENTERS
MACHINING CENTERS FOR ALUMINIUM COMPOSITE PANELS
NOTCHING SAWS
WEDGE CUTTING SAWS AND NOTCH CUTTING SAWS
MITER SAWS FOR ALUMINIUM
PVC PLASTIC MACHINES
PORTABLE MITER SAWS FOR PLASTIC
PORTABLE COPY ROUTER MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
PORTABLE END MILLING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
MITER SAWS FOR PLASTIC
COPY ROUTERS FOR PLASTIC
END MILLING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
WELDING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC
CORNER CLEANING MACHINES FOR PLASTIC PROFILES
DOUBLE MITRE SAWS FOR PLASTIC
BAR PROCESSING CENTERS
GLAZING BEAD SAWS
AUTOMATIC MITRE SAWS FOR PLASTIC
METAL MACHINES
MANUAL METAL SHEET BENDING MACHINE
MANUAL BENDING MACHINES
HYDRAULIC BENDING MACHINES
NON MANDREL BENDERS
PLATE BENDING MACHINES
BORDERING AND TRIMMING MACHINES
HORIZONTAL PRESSES
BELT GRINDING MACHINES
PIPE NOTCHING MACHINES
PIPE POLISHING MACHINES
LASER CUTTING MACHINES
PRESS BRAKES
VERTICAL TURNING CENTERS
MACHINING CENTERS
WOOD MACHINES
GLASS MACHINES
ROBOTICS SPECIAL MACHINERY
Service
Blog
Contact
Blog
- Home
- Blog
- ALUMINIUM PROFILE SAW MACHINE
- ALUMINIUM MACHINE
ALUMINIUM MACHINE

Aluminium Machine – Complete Guide for Cutting, Milling, and Processing
Introduction: What Is an Aluminium Machine?
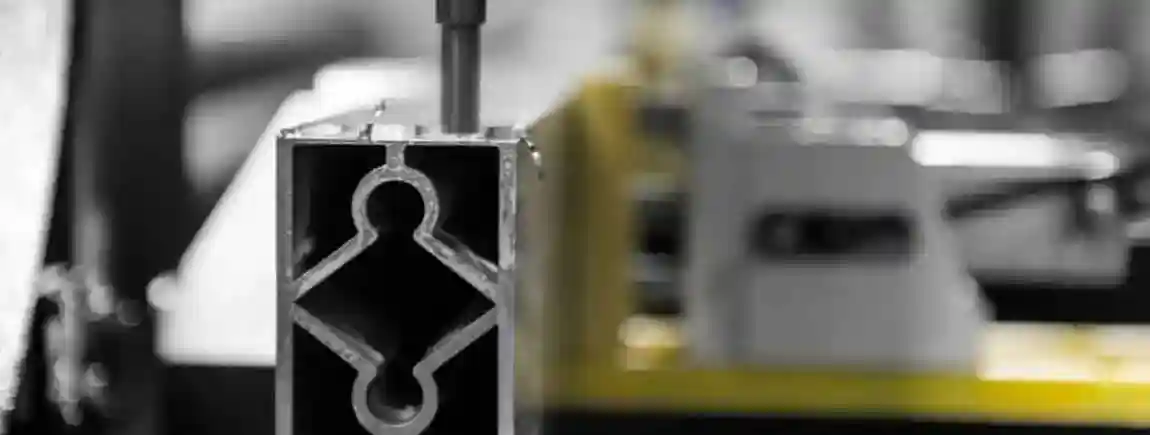
Aluminium is one of the most widely used materials in modern industries. Its light weight, corrosion resistance, and durability make it an essential element in construction, automotive, aerospace, furniture, and electronics. To process this versatile material, industries rely on aluminium machines – specialized equipment designed for cutting, milling, drilling, bending, welding, and machining aluminium with high precision.
An aluminium machine is not one single type of equipment but rather a category of machines that handle the entire aluminium processing cycle, from cutting profiles to complex CNC machining.
Types of Aluminium Machines
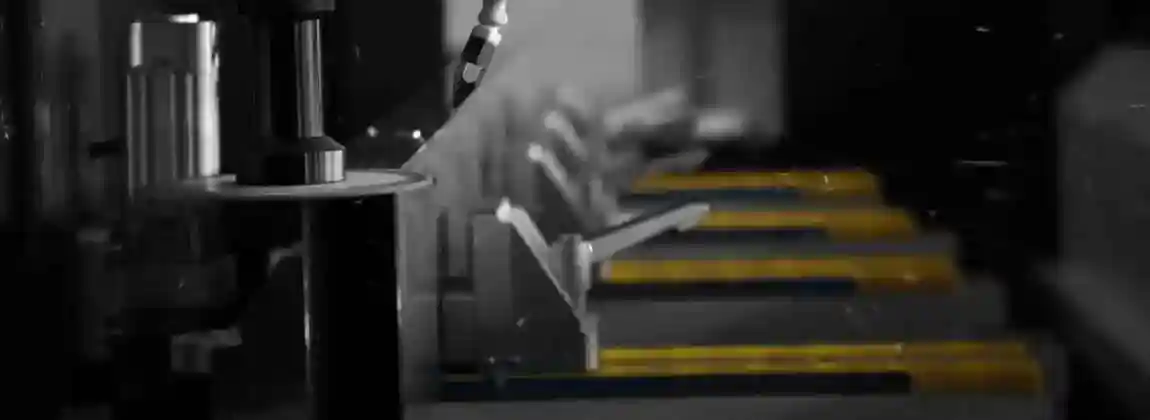
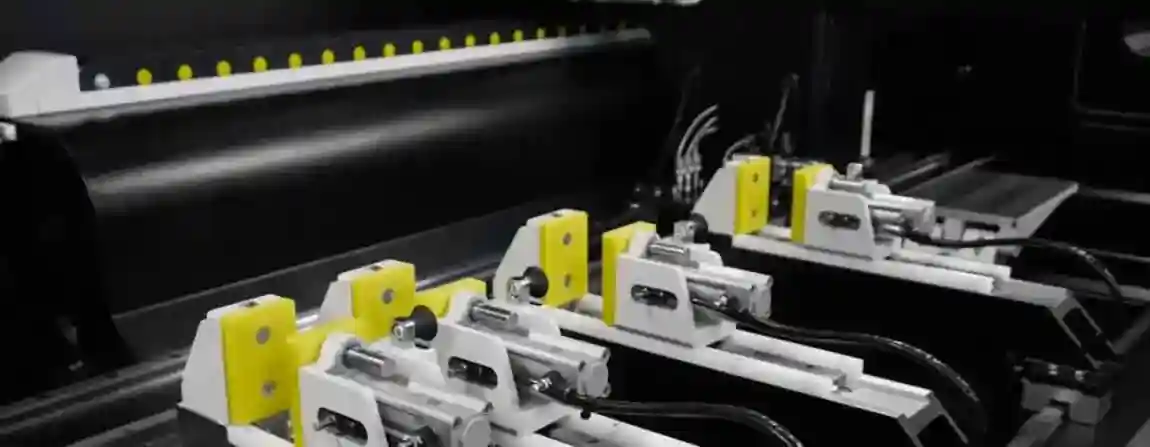
1. Aluminium Cutting Machines
Machines designed to cut aluminium sheets, profiles, and panels. They include manual saws, semi-automatic cutting machines, double head cutting machines, and CNC automatic cutting lines.
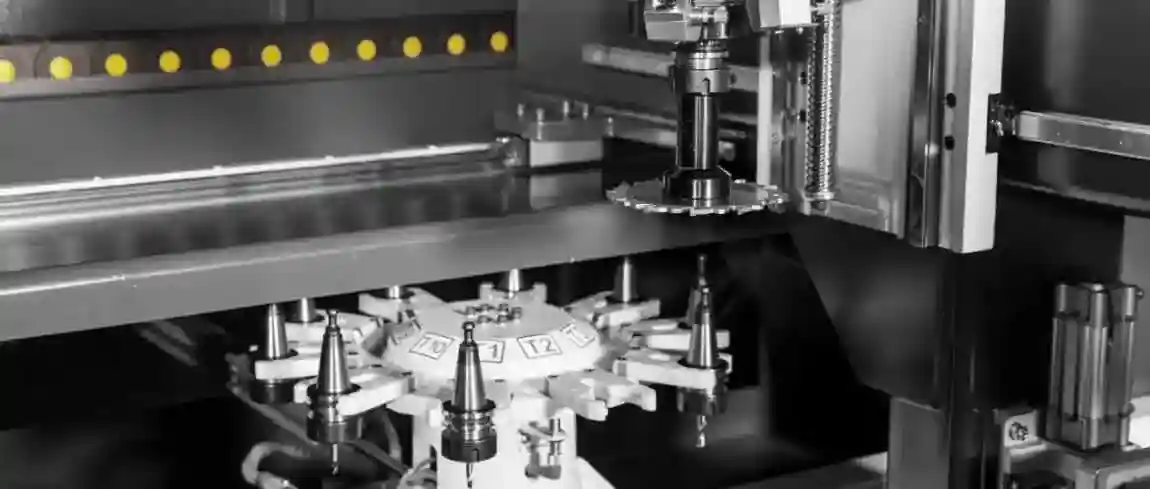
2. Aluminium CNC Machining Centers
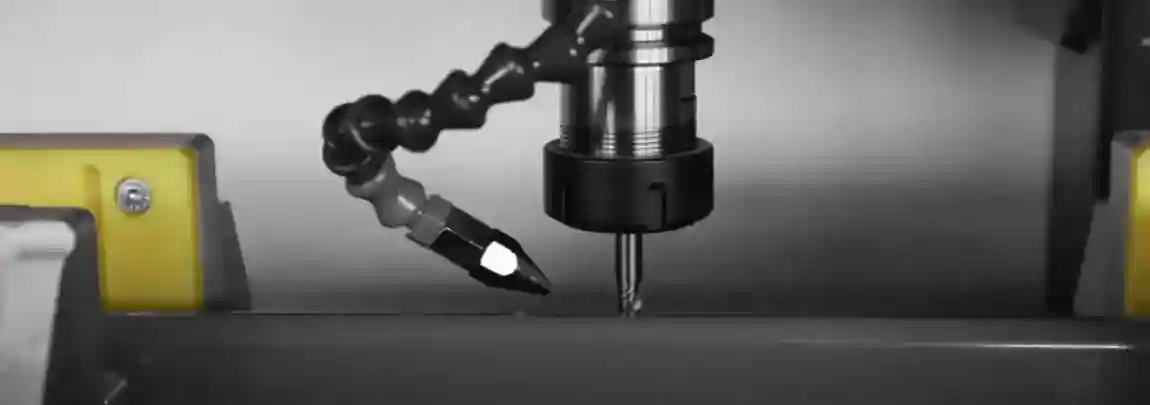
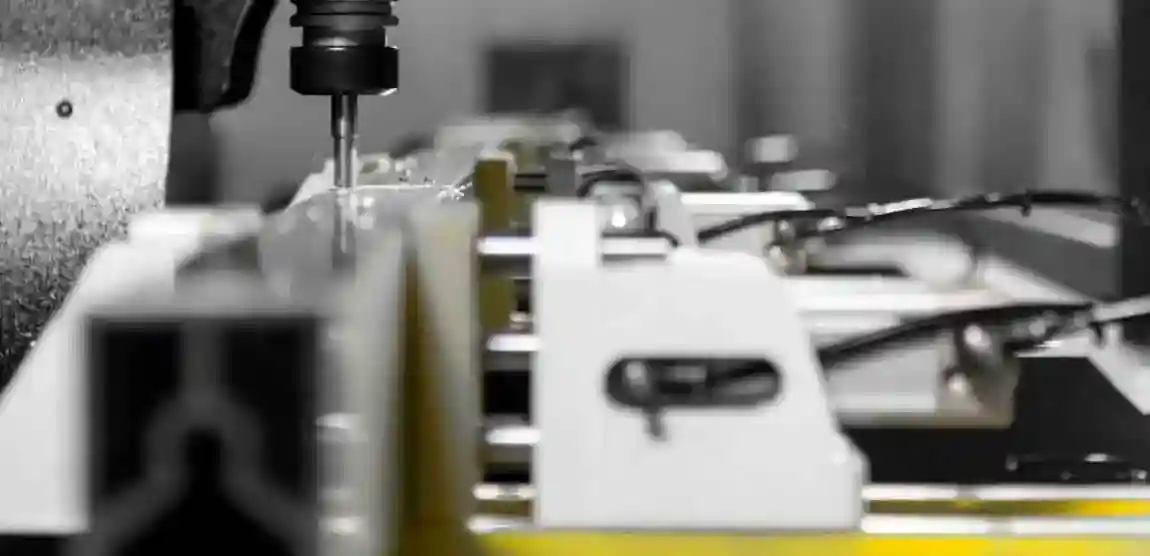
High-precision machines controlled by computer numerical control (CNC). They perform milling, drilling, tapping, and engraving on aluminium profiles and plates. CNC aluminium machines are widely used in window and door manufacturing, aerospace components, and industrial parts.
3. Aluminium Drilling and Milling Machines
Machines specialized in drilling holes and milling slots in aluminium. They are often used in facade construction and extrusion processing.
4. Aluminium Welding Machines
Essential for joining aluminium parts in construction, automotive, and shipbuilding. They include MIG, TIG, and friction welding systems.
5. Aluminium Bending Machines
Designed to bend aluminium profiles and sheets into precise shapes. Common in architectural structures, signage, and furniture.
6. Aluminium Extrusion Processing Machines
Equipment that handles extruded aluminium profiles. Includes cutting, notching, and machining systems for large-scale production.
7. Aluminium Polishing and Finishing Machines
Used to provide smooth surfaces, decorative finishes, or protective coatings to aluminium parts.
Applications of Aluminium Machines
Aluminium machines are used across multiple industries:
-
Construction and Architecture: aluminium windows, doors, curtain walls, and facades.
-
Automotive Industry: lightweight vehicle frames, engine parts, and body components.
-
Aerospace: high-strength aluminium alloys for aircraft panels and parts.
-
Furniture Manufacturing: aluminium frames, tables, and decorative profiles.
-
Electronics: housings, panels, and precision enclosures.
-
Renewable Energy: aluminium parts for solar panels and wind turbines.
Benefits of Using Aluminium Machines
-
High Precision – accurate cuts and machining for consistent results.
-
Efficiency – faster production cycles compared to manual processing.
-
Durability – machines built for industrial use with long service life.
-
Flexibility – capable of handling different shapes, sizes, and alloys.
-
Cost Savings – reduced material waste and labor time.
-
Scalability – suitable for both small workshops and large factories.
Factors to Consider Before Buying an Aluminium Machine
-
Production Scale: small workshop vs. large industrial plant.
-
Type of Operations: cutting, drilling, CNC machining, bending, or welding.
-
Automation Level: manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic CNC.
-
Machine Size and Capacity: maximum profile or sheet dimensions.
-
Software Integration: CAD/CAM compatibility for CNC operations.
-
Budget: balancing initial investment with long-term ROI.
Future Trends in Aluminium Machines
With the rise of automation and Industry 4.0, aluminium machines are becoming more advanced. Modern systems integrate:
-
CNC and robotic automation for high-speed production.
-
IoT-based monitoring for predictive maintenance.
-
Eco-friendly cooling and lubrication systems.
-
Advanced CAD/CAM integration for complex designs.
These innovations make aluminium machines more efficient, sustainable, and connected.
Conclusion: The Role of Aluminium Machines in Modern Industry
The aluminium machine is a key driver of industrial progress. From simple hand cutting machines to multi-axis CNC machining centers, they enable manufacturers to produce high-quality, lightweight, and durable aluminium components for global markets.
Investing in the right aluminium machine ensures productivity, precision, and competitiveness in industries where efficiency and quality are essential.
- Aluminium Machine
- Aluminium Machines
- CNC Aluminium Machine
- Automatic Aluminium Machine
- Manual Aluminium Machine
- Aluminium Cutting Machine
- Aluminium Profile Machine
- Aluminium Extrusion Machine
- Aluminium Processing Machine
- Aluminium Machining Center
- Aluminium Milling Machine
- Aluminium Drilling Machine
- Aluminium Welding Machine
- Aluminium Bending Machine
- Aluminium Fabrication Machine
- Aluminium Window Machine
- Aluminium Door Machine
- Aluminium Sheet Machine
- Aluminium Panel Machine
- Industrial Aluminium Machine
 GERMANY
GERMANY ENGLISH
ENGLISH FRANCE
FRANCE SPAIN
SPAIN PORTUGAL
PORTUGAL